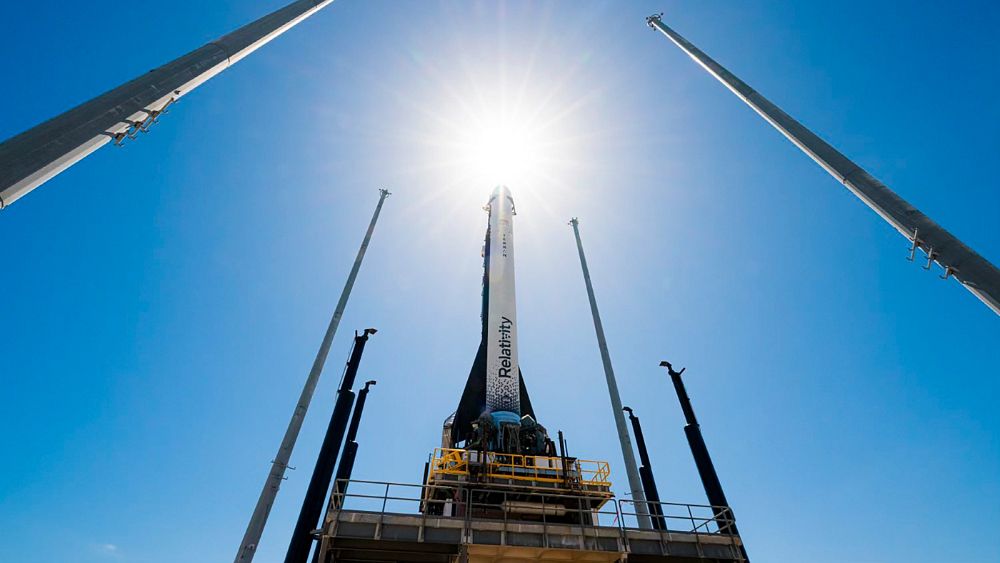
A rocket made almost entirely of 3D-printed parts finally launched on Wednesday night, but it faced an engine issue three minutes into flight and failed to reach orbit.
There was nothing aboard Relativity Space’s test flight except for the company’s first metal 3D print made six years ago.
The start-up wanted to put the souvenir into a 200-km-high orbit for several days before having it plunge through the atmosphere and burn up along with the upper stage of the rocket.
As it turned out, the first stage did its job following lift-off from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, USA – a former missile test site – and separated as planned.
But the upper stage appeared to ignite and then shut down, sending it crashing into the Atlantic.
Relativity had been aiming to launch the rocket earlier this month, but two prior launch attempts were foiled by issues that included unsatisfactory fuel pressure and getting the propellant to sufficiently cold temperatures.
Although the upper stage malfunctioned and the mission did not reach orbit, “maiden launches are always exciting and today’s flight was no exception,” Relativity Space launch commentator Arwa Tizani Kelly said after Wednesday’s launch.

Most of the 33-m rocket, including its engines, came out of the company’s huge 3D printers in Long Beach, California.
Relativity Space said 3D-printed metal parts made up 85 per cent of the rocket, named Terran. Larger versions of the rocket will have even more and also be reusable for multiple flights.
Other space companies also rely on 3D printing, but the pieces make up only a small part of their rockets.
Founded in 2015 by a pair of young aerospace engineers, Relativity Space has attracted the attention of investors and venture capitalists.